Digital Sovereignty in the Age of Artificial Intelligence:The 2026 Strategic Guide for Executives


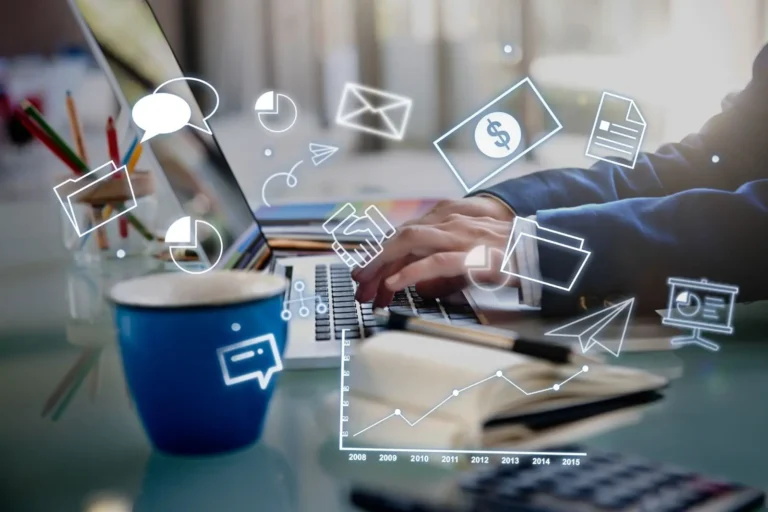
cybersecurity is no longer a complementary function of the IT department; it has become a core pillar of business strategy and digital sovereignty. As we stand in mid-2026, the digital landscape is undergoing an unprecedented radical transformation, where three major forces intersect: the full maturity of generative artificial intelligence technologies, the entrenchment of hybrid work models as a global standard, and the escalating complexity of cyber threats.
This article presents an in-depth, data-driven analysis of how executives and technology leaders navigate this rugged terrain like VPN, with a focus on building a “trust infrastructure” that goes beyond traditional solutions.
The Economic Landscape of Threats: A $10.5 Trillion Bill
Let us begin with the shocking economic facts. Estimates indicate that the global cost of cybercrime will reach USD 10.5 trillion by the end of 2026. If cybercrime were a country, it would possess the third-largest economy in the world after the United States and China. This figure is not merely a statistic; it represents the largest transfer of economic wealth in history, putting incentives for innovation and investment at risk.
Reports further predict that this cost will surge to USD 15.63 trillion by 2029, driven by the increasing sophistication of ransomware attacks and the targeting of supply chains. For startups and large enterprises alike, this means that cybersecurity budgets are no longer “operational expenses” but rather “investments in survival.”
The Hybrid Work Paradox: Freedom Versus Control
By 2026, remote work is no longer an “experiment” but an entrenched institutional reality. Statistics indicate that approximately 32.6 million Americans work remotely, representing 22% of the workforce, while 83% of employees globally prefer hybrid work models.
This permanent shift has created what we call a “fragmented security perimeter.” In the past, company data was protected within office walls and fortified servers. Today, data flows through unsecured home Wi-Fi networks, airport cafés, and co-working spaces in Bali or Lisbon.
Here lies the dilemma: how do you grant your teams the freedom to work from anywhere without opening your organization’s doors to attackers? The answer lies in adopting a Zero Trust philosophy and equipping employees with strong, easy-to-use personal protection tools.
Decentralized Defense Tools: The Rise of VPNs as a Strategic Necessity
In the face of this fragmented perimeter, the virtual private network (VPN) market has witnessed massive growth, valued at USD 45 billion in 2024 and expected to reach USD 77 billion by 2026. VPNs are no longer merely tools for bypassing blocked websites; they have become the first line of defense for encrypting data in transit.
However, leaders face a challenge in selecting tools that balance security with ease of use to ensure employee compliance. Complex tools that require lengthy sign-up procedures are often ignored in favor of speed.
Here we see the rise of a new type of solution that prioritizes absolute privacy and accessibility. For example, solutions such as VPN for Android & VPN for iOS have emerged as interesting options in this space. What distinguishes this type of tool in 2026 is its departure from traditional registration complexities; some of its services (especially free or trial versions) offer instant access without the need to enter personal data or create complex accounts.
This no-log policy model and AES-256 encryption, offered by services such as Planet VPN and others, provide a vital balance for agile teams: military-grade data protection combined with flexibility that allows marketers to test geo-specific content and developers to access global resources without leaving a digital footprint. Integrating such flexible tools into an organization’s security policy reduces the phenomenon of Shadow IT by providing approved and secure alternatives for employees.
Artificial Intelligence: A Double-Edged Sword
It is impossible to discuss 2026 without addressing artificial intelligence. While companies use AI to detect threats more quickly (thereby reducing the average cost of data breaches and the time required to contain them), attackers are using the same technology to launch more precise attacks.
- AI-powered phishing: Phishing attacks have surged by an astonishing 1,265%, as large language models (LLMs) are used to craft highly convincing emails that are difficult for humans to distinguish.
- Data poisoning: The upcoming threat in 2026 and beyond is attackers’ attempts to contaminate the data used to train corporate AI models, leading to incorrect or catastrophic automated decisions.
Counter-strategy: Organizations must invest in “AI firewalls” and train employees not only in traditional information security, but also in Prompt Security—how to interact with AI tools without leaking company secrets.
Beyond Compliance: Privacy as a Competitive Advantage
Previously, compliance with regulations such as GDPR was merely a box to be checked. In 2026, privacy has become a product and a competitive advantage. Consumers and B2B clients choose partners who can demonstrate “digital sovereignty” over their data.
This means that the security tools your company uses—from cloud service providers to VPN services and identity management tools—must undergo rigorous scrutiny. Relying on privacy-respecting tools (such as those that do not retain user activity logs) strengthens a company’s legal and ethical position in the eyes of its customers.
Roadmap to the Future: 2026 and Beyond
As we look ahead to 2026, executives must prepare for the next wave of technologies:
- Quantum Computing: Current encryption may become obsolete within a decade. Leading companies are already exploring “quantum-resistant” encryption algorithms.
- Blockchain in cybersecurity: In line with Coruzant’s vision of emerging technologies, we expect deeper integration of blockchain technology for identity verification (Decentralized Identity) and data integrity, making record tampering nearly impossible.
- Hyper-automation: Autonomous systems will handle 90% of security alerts, leaving human analysts to focus on complex strategic threats.
Conclusion
In 2026, cybersecurity is not a technical problem; it is an existential business challenge. The ability to work from anywhere, use artificial intelligence boldly, and protect corporate assets simultaneously is what will distinguish leaders from followers. Whether through adopting a Zero Trust architecture, integrating flexible and powerful protection tools such as Planet VPN to secure a mobile workforce, or investing in AI-driven defenses, the message is clear: trust is the new currency, and security is the bank that safeguards it.
Also Read-Gradding Introduces AI-Powered IELTS Practice Tech for Smarter Preparation